Portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 1
Short description of portfolio item number 2 
arXiv preprint, 2019
A new attention mechanism that considers phrases as attention entities instead of individual tokens in MT.
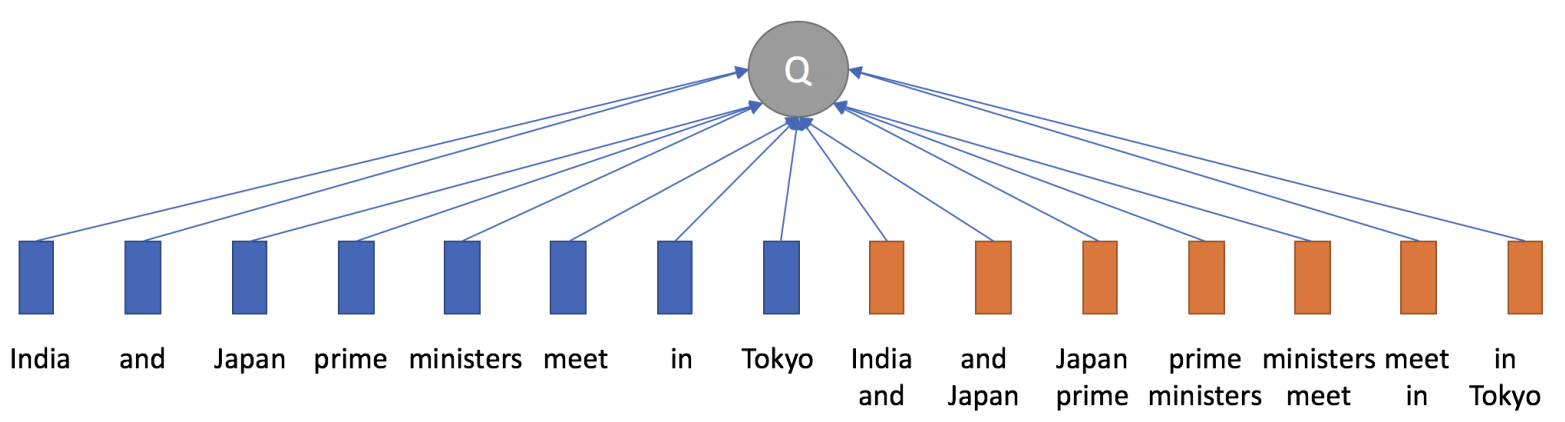
Citation: Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty, Thank-Tung Nguyen (2019). Enhancing Attention with Explicit Phrasal Alignments.
Paper Link: https://openreview.net/forum?id=BygPq6VFvS
NAACL 2019 - Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2019
Leverage abundant unlabeled conversational data and the available labeled data from synchronous domain.
Citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen*, Tasnim Mohiuddin*, Shafiq Joty* (2019). Adaptation of Hierarchical Structured Models for Speech Act Recognition in Asynchronous Conversation. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies.
Paper Link: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N19-1134/
Cognitive Computation, 2019
Design a novel multi-relation structure RNN model with a hierarchical attention mechanism to capture not only the conventional temporal dependencies but also the explicit multi-relation topology dependencies.
Citation: Hongyun Cai, Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Yan Li, Vincent W Zheng, Binbin Chen, Gao Cong, Xiaoli Li (2019). In Cognitive Computation
Paper Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12559-019-09690-8
ACL 2020 - The 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020
Using differentiable windows to perform local attentions greatly improve performance of machine translation and language modeling.
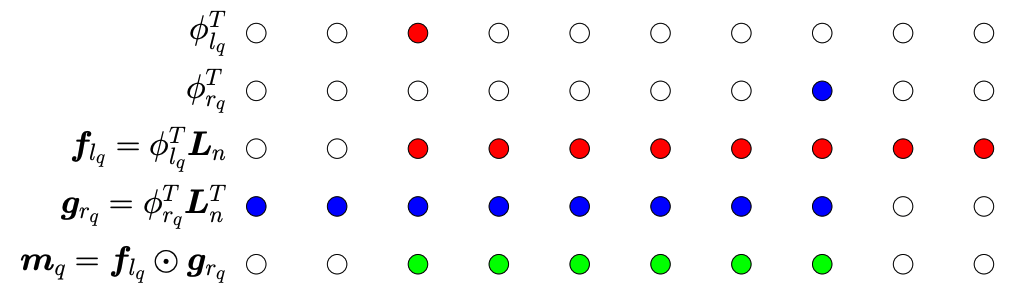
Citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen*, Xuan-Phi Nguyen*, Shafiq Joty & Xiaoli Li (2020). Differentiable Window for Dynamic Local Attention. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Paper Link: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.acl-main.589/
ACL 2020 - The 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020
A new parsing method that employs pointing mechanism to perform top-down decoding. The method is competitive with the state-of-the-art while being faster.
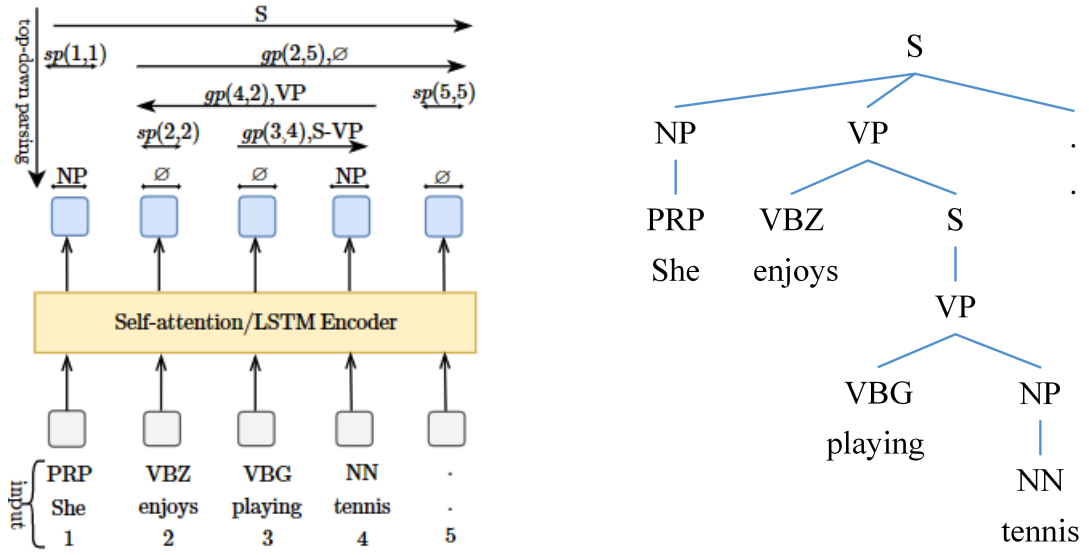
Citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty & Xiaoli Li (2020). Efficient Constituency Parsing by Pointing. In Proceedings of the 58th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Association for Computational Linguistics.
Paper Link: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/2020.acl-main.301/
NAACL 2021 - Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, 2021
We introduce a novel top-down end-to-end formulation of document level discourse parsing in the Rhetorical Structure Theory (RST) framework. In this formulation, we consider discourse parsing as a sequence of splitting decisions at token boundaries and use a seq2seq network to model the splitting decisions. Our framework facilitates discourse parsing from scratch without requiring discourse segmentation as a prerequisite; rather, it yields segmentation as part of the parsing process. Our unified parsing model adopts a beam search to decode the best tree structure by searching through a space of high scoring trees. With extensive experiments on the standard RST discourse treebank, we demonstrate that our parser outperforms existing methods by a good margin in both end-to-end parsing and parsing with gold segmentation. More importantly, it does so without using any handcrafted features, making it faster and easily adaptable to new languages and domains.
Citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty, Xiaoli Li. RST Parsing from Scratch. In Proceedings of the 2021 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies.
Paper Link: https://aclanthology.org/2021.naacl-main.128.pdf
38th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2021
A novel strategy to improve unsupervised MT by using back-translation with multiple models.

Citation: Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty,Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Wu Kui, & Ai Ti Aw (2021). Multi-Agent Cross-Translated Diversification for Unsupervised Machine Translation arXiv preprint arXiv:2006.02163.
Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.02163
ACL 2021 - The 59th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2021
We introduce a generic seq2seq parsing framework that casts constituency parsing problems (syntactic and discourse parsing) into a series of conditional splitting decisions. Our parsing model estimates the conditional probability distribution of possible splitting points in a given text span and supports efficient top-down decoding, which is linear in number of nodes. The conditional splitting formulation together with efficient beam search inference facilitate structural consistency without relying on expensive structured inference. Crucially, for discourse analysis we show that in our formulation, discourse segmentation can be framed as a special case of parsing which allows us to perform discourse parsing without requiring segmentation as a pre-requisite. Experiments show that our model achieves good results on the standard syntactic parsing tasks under settings with/without pre-trained representations and rivals state-of-the-art (SoTA) methods that are more computationally expensive than ours. In discourse parsing, our method outperforms SoTA by a good margin.
Citation: Thanh-Tung Nguyen, Xuan-Phi Nguyen, Shafiq Joty, Xiaoli Li
Paper Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.15760
Published:
This is a description of your talk, which is a markdown files that can be all markdown-ified like any other post. Yay markdown!
Published:
This is a description of your conference proceedings talk, note the different field in type. You can put anything in this field.
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.